向量学习
Posted May 13, 2024 by wangzx ‐ 16 min read
Next ⇨本文是想通过案例来学习 vectorize 的 使用、效果,以加深对这项技术的理解。 这个例子是 参考: ucasfl:ClickHouse 系列 - 向量化执行引擎介绍 中介绍的 countBytes 函数, 我使用 rust portable Simd 库来进行练习。
代码可以 从这里访问:playground
或者参考如下代码:
#![feature(portable_simd)]
#![feature(stdsimd)]
use std::mem::{size_of};
use std::simd::{SimdPartialEq, ToBitMask};
use std::simd::{u8x16, u8x32, u8x64};
use std::simd::Simd;
fn fill_data(bytes: &mut [u8]) {
for i in 0..bytes.len() {
let random = rand::random::<u16>();
bytes[i] = if random % 8 < 4 { 0 } else { random as u8 };
}
}
fn main() {
let mut bytes = [0; 1024];
let random = rand::random::<usize>();
fill_data(&mut bytes);
{
run1("countNonZero_inline", 1, 1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZero_inline(&bytes)
});
}
println!();
{
run1("countNonZeroV128_countOnes_inline", 16,1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZeroV128_countOnes_inline(&bytes)
});
run1("countNonZeroV256_countOnes_inline", 32,1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZeroV256_countOnes_inline(&bytes)
});
run1("countNonZeroV512_countOnes_inline", 64,1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZeroV512_countOnes_inline(&bytes)
});
}
println!();
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
{
run1("countNonZeroV128_popcnt_intrins_inline", 16, 1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZeroV128_popcnt_intrins_inline(&bytes)
});
run1("countNonZeroV256_popcnt_intrins_inline", 32, 1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZeroV256_popcnt_intrins_inline(&bytes)
});
// require 256bit AVX2
run1("countNonZeroV256_popcnt_intrins_x86", 32, 1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
unsafe { countNonZeroV256_popcnt_intrins_x86(&bytes) }
});
run1("countNonZeroV512_popcnt_intrins_inline", 64, 1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZeroV512_popcnt_intrins_inline(&bytes)
});
// require 512bit AVX2
run1("countNonZeroV512_popcnt_intrins_x86", 32, 1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
unsafe { countNonZeroV512_popcnt_intrins_x86(&bytes) }
});
}
println!();
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
{
run1("countNonZeroV128_popcntAsm_inline", 16, 1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZeroV128_popcntAsm_inline(&bytes)
});
run1("countNonZeroV256_popcntAsm_inline", 32, 1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZeroV128_popcntAsm_inline(&bytes)
});
run1("countNonZeroV512_popcntAsm_inline", 64, 1_000_000, || {
bytes[random % 1024] += 1;
countNonZeroV128_popcntAsm_inline(&bytes)
});
}
println!();
}
fn run1<F>(label: &str, width: usize, loops: usize, mut f: F) where F: FnMut()->usize {
let time0 = std::time::Instant::now();
let mut time1 = time0;
let end = time0 + std::time::Duration::from_secs(5);
let mut sum = 0;
let mut n = 0usize;
loop {
for _i in 0..loops {
sum += f();
}
n += loops;
time1 = std::time::Instant::now();
if time1 >= end {
break;
}
}
let elapsed = time1 - time0;
let avg = elapsed.as_nanos() as f64 / n as f64;
println!("{label:32}\tlane width: {width}\tsum:{sum:16}\ttimes:{elapsed:?}\ttime:{avg:?}ns/iter");
}
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZero_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
let mut count = 0;
for &byte in bytes {
if byte != 0 {
count += 1;
}
}
count
}
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZero(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
let mut count = 0;
for &byte in bytes {
if byte != 0 {
count += 1;
}
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZeroV128_popcnt_intrins_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = u8x16;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt64(bits as i64) as usize };
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZeroV256_popcnt_intrins_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = u8x32;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt64(bits as i64) as usize };
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(always)]
unsafe fn countNonZeroV256_popcnt_intrins_x86(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
use core::arch::x86_64::*;
type VT = __m256i;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = _mm256_setzero_si256() ;
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = _mm256_loadu_epi8(bytes.as_ptr().add(i) as *const i8);
let mask = _mm256_cmp_epi8_mask(chunk, zero, _MM_CMPINT_NE);
count += mask.count_ones() as usize;
i += 32;
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZeroV512_popcnt_intrins_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = u8x64;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt64(bits as i64) as usize };
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(always)]
unsafe fn countNonZeroV512_popcnt_intrins_x86(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
use core::arch::x86_64::*;
type VT = __m512i;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = _mm512_setzero_si512() ;
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = _mm512_loadu_epi8(bytes.as_ptr().add(i) as *const i8);
let mask = _mm512_cmp_epi8_mask(chunk, zero, _MM_CMPINT_NE);
count += mask.count_ones() as usize;
i += 64;
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
////
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZeroV128_popcnt_intrins(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = u8x16;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt64(bits as i64) as usize };
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZeroV256_popcnt_intrins(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = u8x32;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt64(bits as i64) as usize };
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZeroV512_popcnt_intrins(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = u8x64;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt64(bits as i64) as usize };
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZeroV128_countOnes_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = Simd<u8, 16>;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += bits.count_ones() as usize;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZeroV256_countOnes_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = Simd<u8, 32>;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += bits.count_ones() as usize;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZeroV512_countOnes_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = Simd<u8, 64>;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += bits.count_ones() as usize;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
//// no-inline
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZeroV128_countOnes(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = Simd<u8, 16>;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += bits.count_ones() as usize;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZeroV256_countOnes(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = Simd<u8, 32>;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += bits.count_ones() as usize;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZeroV512_countOnes(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
type VT = Simd<u8, 64>;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
count += bits.count_ones() as usize;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZeroV128_popcntAsm_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
use core::arch::asm;
type VT = u8x16;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
let n: usize;
// count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt32(bits as i32) as usize };
unsafe { asm! {
"popcnt {y}, {x}", x = in(reg) bits, y = out(reg) n
} }
count += n;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZeroV256_popcntAsm_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
use core::arch::asm;
type VT = u8x32;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
let n: usize;
// count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt32(bits as i32) as usize };
unsafe { asm! {
"popcnt {y}, {x}", x = in(reg) bits, y = out(reg) n
} }
count += n;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(always)]
fn countNonZeroV512_popcntAsm_inline(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
use core::arch::asm;
type VT = u8x64;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
let n: usize;
// count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt32(bits as i32) as usize };
unsafe { asm! {
"popcnt {y}, {x}", x = in(reg) bits, y = out(reg) n
} }
count += n;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
/// no-inline
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZeroV128_popcntAsm(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
use core::arch::asm;
type VT = u8x16;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
let n: usize;
// count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt32(bits as i32) as usize };
unsafe { asm! {
"popcnt {y}, {x}", x = in(reg) bits, y = out(reg) n
} }
count += n;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZeroV256_popcntAsm(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
use core::arch::asm;
type VT = u8x32;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
let n: usize;
// count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt32(bits as i32) as usize };
unsafe { asm! {
"popcnt {y}, {x}", x = in(reg) bits, y = out(reg) n
} }
count += n;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
#[inline(never)]
fn countNonZeroV512_popcntAsm(bytes: &[u8]) -> usize {
use core::arch::asm;
type VT = u8x64;
let mut count = 0;
let mut i = 0;
let zero = VT::splat(0);
while i + size_of::<VT>() <= bytes.len() {
let chunk = VT::from_slice(&bytes[i..]);
let cmp = chunk.simd_ne(zero);
let bits: u64 = cmp.to_bitmask() as u64;
let n: usize;
// count += unsafe { std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt32(bits as i32) as usize };
unsafe { asm! {
"popcnt {y}, {x}", x = in(reg) bits, y = out(reg) n
} }
count += n;
i += size_of::<VT>();
}
if i < bytes.len() {
count += countNonZero_inline(&bytes[i..]);
}
count
}
- 128bit: u8x16
- 256bit: u8x32
- 512bit: u8x64
这个实现中,对如何进行整数的1位统计分别使用了3种方法:
- count_ones。看rust得实现,采用的算法并不算太高效
- 尝试使用 std::arch::x86_64::_popcnt64(bits as i64)
- 尝试使用 asm 嵌入 popcnt 指令。
后面发现,其实可以使用 -Ctarget-cpu=native 来识别 popcnt 特性,从而自动生成 popcnt的代码,这种情况下,可以获得很好的执行效果。
分别在3个平台上进行了测试:
- M1-MAX
- X86 on M1-MAX(Rosetta 2)
- X86(内部虚拟机)
- X86(阿里云 ecs.c7.xlarge型号,CPU为:Intel Xeon(Ice Lake) Platinum 8369B)
- ecs.c7.xlarge,启用 -Ctarget-cpu=native
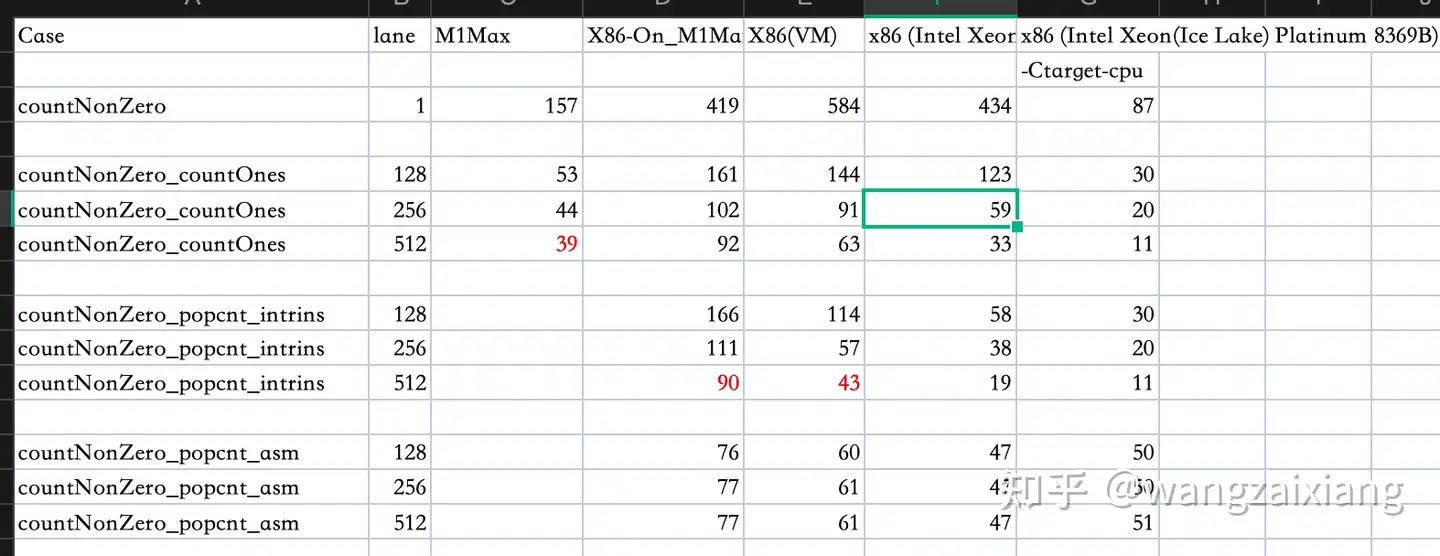
更新:
- 在 x86 AVX512上,使用
cargo +nightly rustc --release -- -Ctarget-cpu=native选项编译后的性能更佳。应该是使用到了当前CPU的全部能力, 512bit向量下,达到了11.7ns。cargo +nightly rustc -Z build-std --target x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu --release -- -Ctarget-cpu=native
结论分析:
- 向量化的版本相比普通循环的版本,有接近10倍的提升。(M1 提升:4倍,X86提升:9倍)portable_simd 实际使用的是 128bit 的向量, 但可以使用256/512位的API,此时,它会进行展开。
- 我之前有个误解,portable_simd无法使用到 AVX512等能力。实际上并不然,只要编译时指定 target-cpu,是可以使用到 avx2, avx512等向量能力的。 portable_simd 是开发向量化算法首选,毕竟可移植性是一个很重要的需求。
- 在部份场合下,rustc会自动向量化,简单场景下效果会和手动向量化效果差不多。但有不少限制,复杂一些算法,可能无法自动向量化。
- 尝试使用 x86 私有的 256位向量/512位向量能力,发现性能反而有下降,查看原因是 rustc 没有为 mm_xxx intrinsc 指令生成内联, 产生了 function call 的开销,这导致了性能的下降。
- 编写测试代码时,前面的版本,inline时进行了过度的优化(指针对当前的场景进行了特定的优化),其不具备可复制性,干扰了测试。 调整后的测试数据要好理解很多。(之前的部份优化,导致 512bit 可以优化到4n s 以内,后实际发现是测试代码触发了rustc进行了逻辑优化, 少执行了不少循环。调整后的代码增加了数据的混乱,避免过度优化)。
- 使用嵌入汇编后,可能会影响编译器的进一步优化,在案列中,asm版本,在支持 AVX512的CPU上并非最佳,我估计是没有进行循环展开导致的。
后续,我会收集基于向量计算的一系列算法,整理一个提纲,例如:
- C++中的向量计算https://www.zhihu.com/question/450069375/answer/3258826060?utm_psn=1714201317017481216
- hash 向量算法:是否可以设计一个可基于 SIMD 的hash算法(不是对单个值计算hash,而是对向量计算hash向量)?
- hash join的 向量算法
- 40x faster hash joiner with vectorized execution
- 源头:Balancing vectorized query execution with bandwidth-optimized storage (已收藏到 ivySCI 库中第5.4节:Optimizing Hash-Join),比较难读。
- A Vectorized Hash-Join
- binary search 的向量算法
- Simd-json 中的向量计算
- 加密解密中的向量计算
- Swiss Table中的向量计算等。Rust HashMap就是基于这个结构的。
- base64Designing a SIMD Algorithm from Scratch · mcyoung非常好的一篇讲解 vectorize 的文章。 以 base64 decode为例构造一个向量实现,我觉得 encode 也适合构造一个向量实现,可以拿来练手。
- Intel 向量指令 https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/docs/intrinsics-guide/index.html
- https://github.com/cloudwego/sonic-rs/blob/main/docs/performance_zh.md sonic-rs如何利用SIMD来加速JSON解析
zig 语言有内置的 SIMD 支持,在 Parker Liu 的专栏,有很多值得学习的干货:
- Zig语言的SIMD并行计算优化初探
- Zig语言的SIMD并行计算优化初探--矩阵转置
- Zig语言的SIMD并行计算优化初探--高通DSP的矩阵转置
- Zig语言的SIMD并行计算优化初探--并行排序
- Zig语言的SIMD并行计算优化初探--混合快速排序
- Zig语言的SIMD并行计算优化初探--多向量并行排序
也欢迎各位帮忙补充你所知道的应用向量计算的算法。